External Data and their importance in an Internationalisation process
Published by Marzia Moccia. .
Planning Internationalisation SME International marketing International marketing
Log in to use the pretty print function and embed function.
Aren't you signed up yet?
signup!
In the previous article The Strategic Importance of Information in SMEs' Business Decisions, we documented how, now more than ever, information represents a strategic resource for better business decisions. Collecting and analyzing accurate and timely information can indeed translate into a real competitive advantage, thanks to its various benefits: a better understanding of the business reality and the reference market context, a timely adaptation to changes, and a strong reinforcement of organizational flexibility through the implementation of more agile models.
The Role of External Data in International Marketing
The role of information becomes even more crucial when it comes to internationalization, where external data sources to the company appear to be of fundamental importance.
In the context of international expansion, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) face challenges of considerable complexity, stemming not only from market diversity but also from various cultural, legal, and economic barriers resulting from a lack of direct knowledge of the target geography, as well as low market experience. Essentially, it becomes necessary for the company's skills system, based on experience and knowledge, to acquire as much information as possible about a new reference context.
External data represent the answer to this need.
External data refers to information collected from sources additional to those of the company's organization. These sources may include market data, macroeconomic data, demographic data, competitor analysis, etc. The collection and analysis of these types of information are functional to provide a broader context than just the company's reference, expanding the analysis with an external perspective.
It is evident how these aspects appear crucial for making informed business decisions when considering unfamiliar contexts, such as foreign markets precisely.
According to major management theories, external data becomes critical knowledge tools for a company for three substantial aspects: environmental analysis, understanding of the competitive context, and formulation of suitable strategies and monitoring.
Environmental Analysis and Understanding of the Competitive Context
Environmental analysis and understanding of the competitive context identify critical processes through which organizations assess and comprehend the external context in the markets they intend to operate in. This process aims to gather detailed and relevant information about the surrounding environment to identify factors of market opportunity, accessibility, and reliability.
The relevant information to collect in this phase pertains to both country macroeconomic conditions and sectoral data, in order to segment the market and evaluate potential demand, as well as the product lifecycle in a given market.
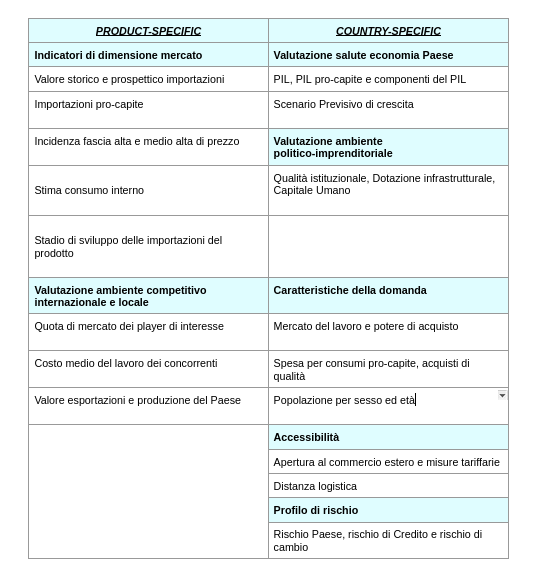
The indicators provided by ExportPlanning are indeed product-specific and country-specific, as summarized in the table below.
Formulation of Suitable Strategies and Monitoring
Strategic planning is the moment when acquired external information combines with internal information to identify the best strategies to implement in target markets. Based on external data, it is indeed possible to tailor marketing, sales, and distribution strategies to respond to the specific dynamics of the target market.
External data also contribute to evaluating the resources and capabilities needed to compete internationally. Analysis of the external context, including data on workforce skills, infrastructure, and regulations, helps identify how internal resources can be aligned with external opportunities and assess the compatibility of internal resources and capabilities with present opportunities.
Another aspect to consider is also the relevance of monitoring. External data, like other sources of information, are dynamic and subject to rapid changes, especially in an increasingly uncertain international context. Companies must be agile in monitoring and responding to new information, quickly adapting to changes to maintain or enhance their competitive position. This includes the ability to anticipate changes and increase organizational flexibility.
In conclusion, a thorough and informed understanding of the foreign market through external data enables businesses to make more solid strategic decisions and successfully adapt to diverse business environments.


