Regionalization and diversification: the case of textile machinery
Anticipating and understanding how the new paradigm of procure-produce-distribute will evolve becomes a key factor for industrial machinery manufacturers
Published by Marzia Moccia. .
Export markets Conjuncture Covid-19 Global economic trendsOne of the most relevant issues today for reading, delineating and anticipating future trajectories of business investment policies undoubtedly relates to the debate on the future of globalization. As anticipated in a previous article (see Regionalization of world trade: current trends), inefficiencies along value chains and the resulting higher costs and delays in international trade of some goods have led some governments, primarily the U.S. administration, to advocate reshoring or more generally regionalization policies in order to secure the supply chain, based on the concepts of resilience, adaptability and flexibility. We talk about regionalization of trade precisely to address the need to shorten production chains, and consequently make them less fragile against external shocks, but also to secure a better time-to-market approach, which allows for greater flexibility and more accurate control of the supply chain.
Anticipating and understanding how the new paradigm to procure-produce-distribute will evolve therefore becomes crucial for mechanical instrument manufacturers, whose strategic internationalization decisions cannot be separated from following the trends and directions of global investment flows and production location choices. Although information on the investment policies carried out by companies around the world is among the most difficult to collect, given the heterogeneity of the assets involved and the different motivations that can determine them, this information is now more crucial than ever for mechanical equipment manufacturers in order to strategically assess the opportunities offered by different markets. In this framework, a particularly relevant case study turns out to be that of textile machinery.
Fig.1 - Africa: an increasingly attractive continent for textile manufacturers
Since mid-century, interest by the world textile industry in the African continent has grown significantly. Indeed, the relative increase in labor costs in several Asian markets, government incentives and easy logistical access to markets in Europe and America, guaranteed by free-access trade agreements, has made Africa a particularly attractive destination for international investors, partly because of its greater geographical proximity. Although in absolute terms, textile production in North Africa and the Horn of Africa still plays a residual role in the world total, in terms of dynamics it has experienced growth very close to that of the Asian continent (Fig.1)
Fig. 1 - Production of textile intermediate goods: Asia vs Africa
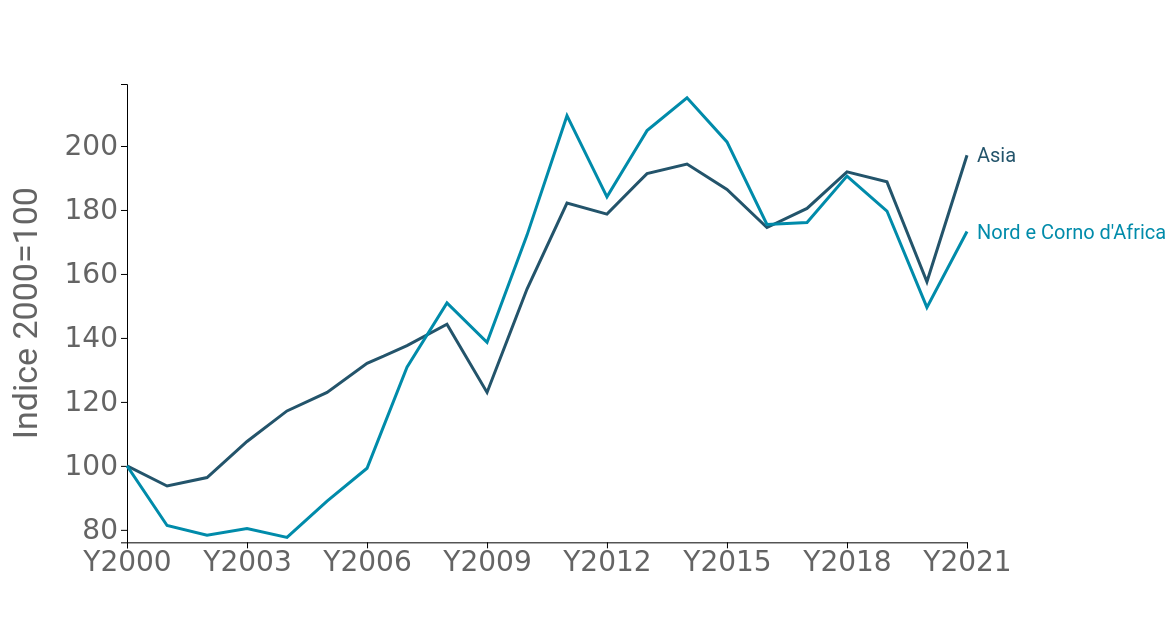
Source: ExportPlanning.
Imports of textile machinery from the area have in fact experienced a significant increase, showing accelerated growth since 2005, interrupted only by the difficulties of the pandemic environment and the extensive penalizations suffered by the Fashion-Personnel System in the post-Covid period (Fig.2)
Fig. 2 - Import of textile machinery: North Africa and Horn of Africa
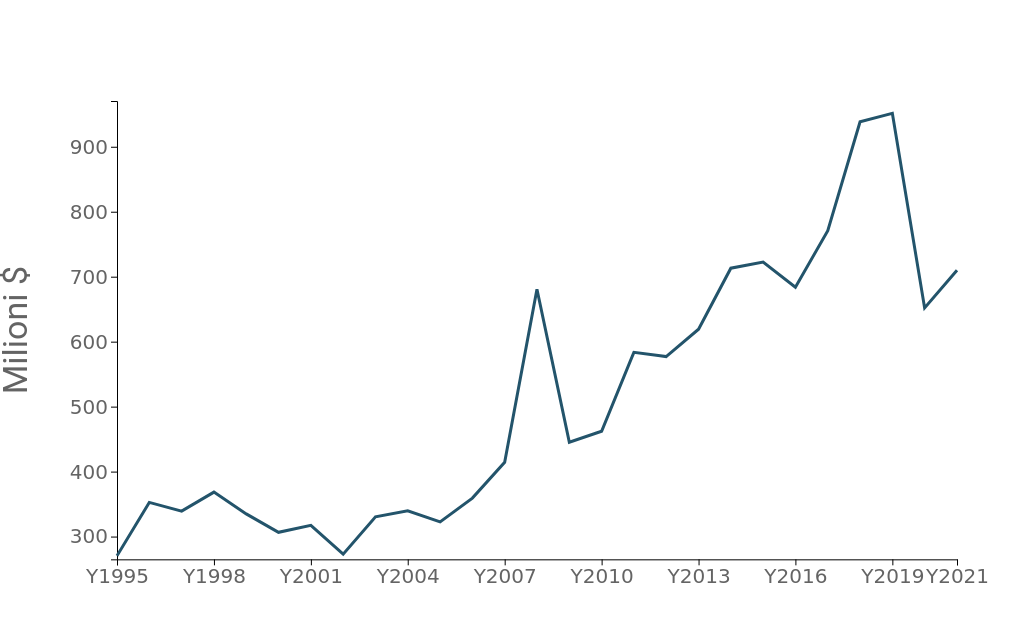
Source: ExportPlanning.
Although they still represent a relatively small market, holding just under 3 percent of world demand for the industry, there is no doubt that the economies of the North African and Horn of Africa regions are candidates to be special observers in the context of reconfiguring global value chains. Indeed, for textile manufacturers, countries in the area could become the cradle of production localizations that can provide greater supply chain security, or simply increase the diversification of companies' supplier portfolios. In both cases, monitoring foreign trade information will be a particularly relevant activity to read the changes taking place and the opportunities offered by different markets to industrial machinery manufacturers.


